문제 : https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/23288
23288번: 주사위 굴리기 2
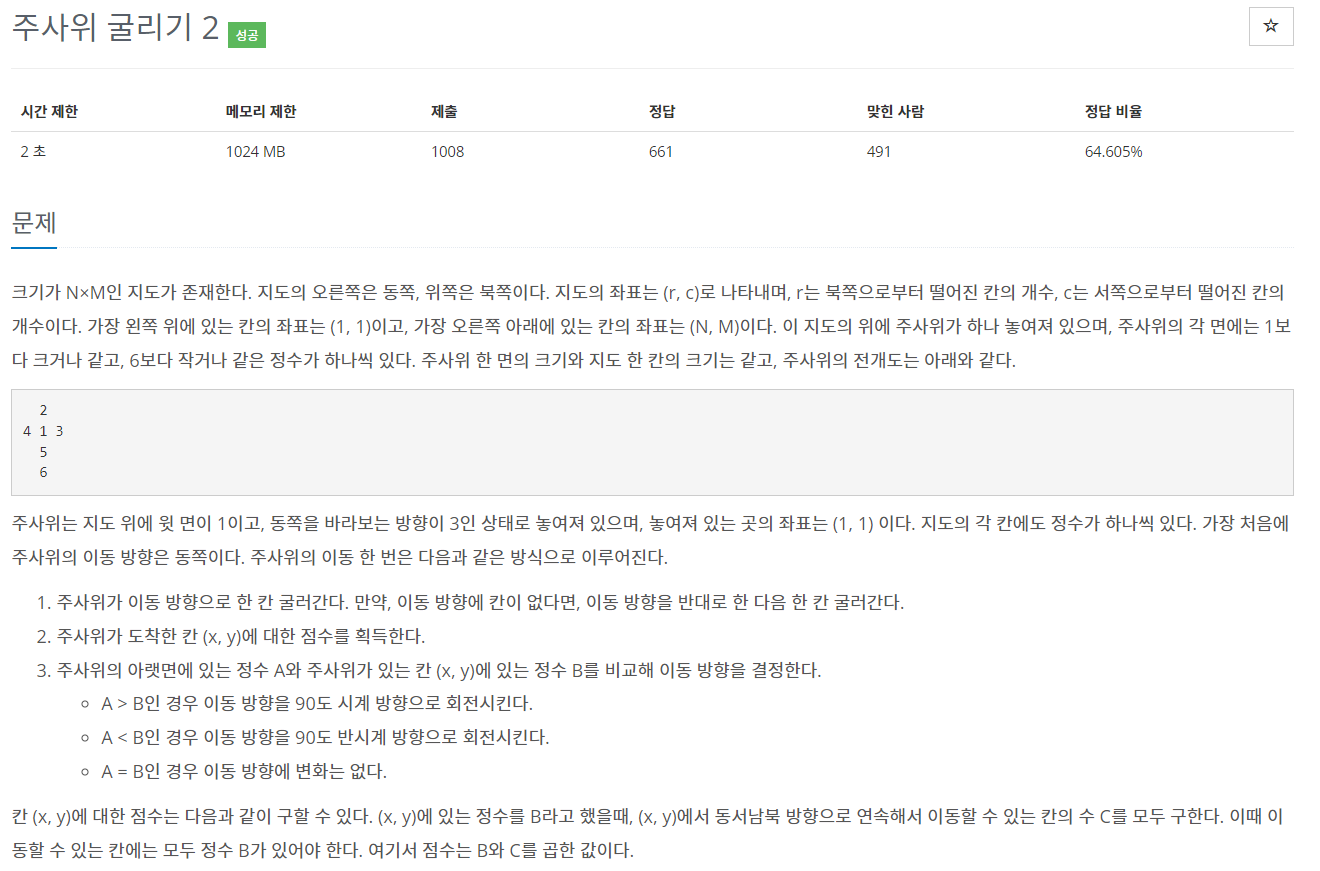
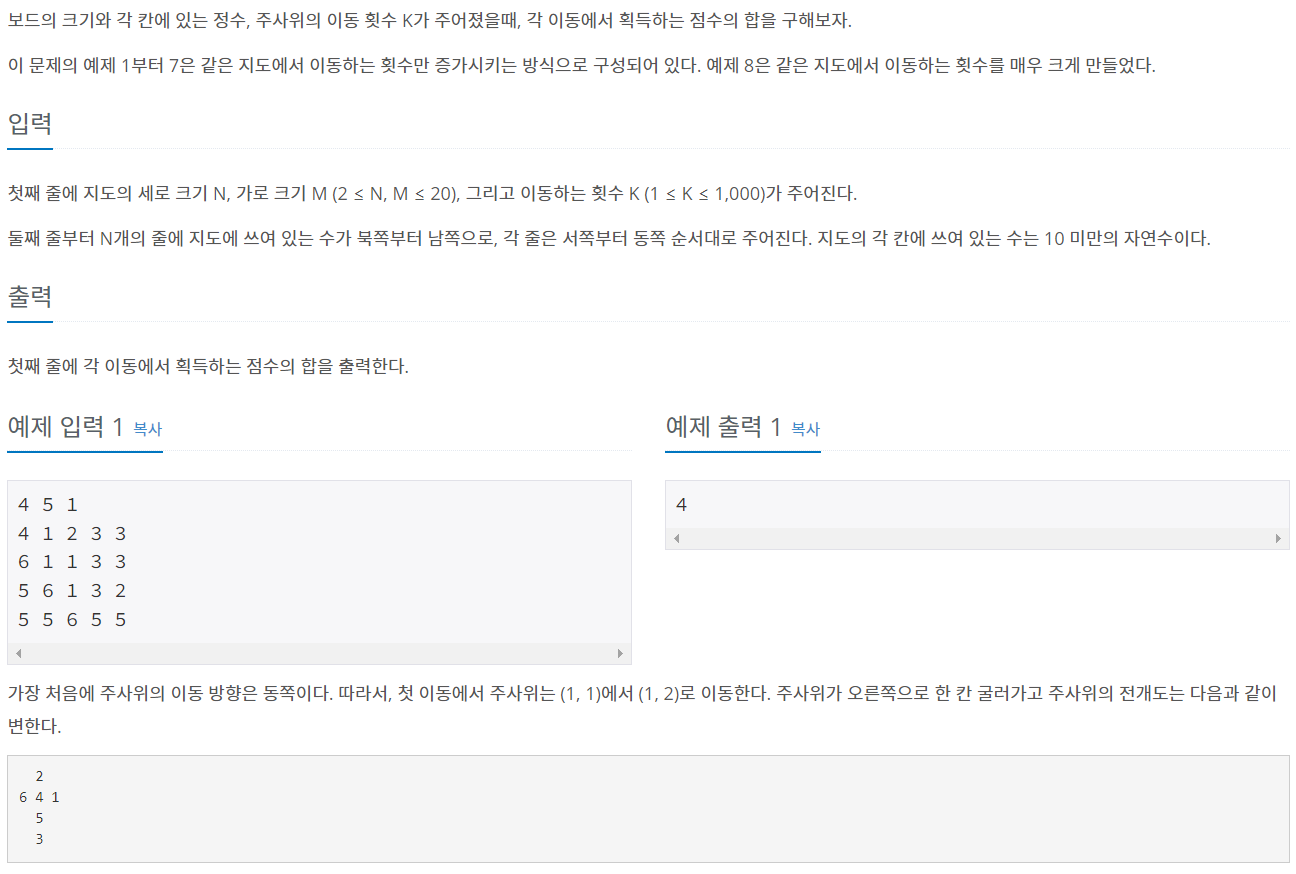
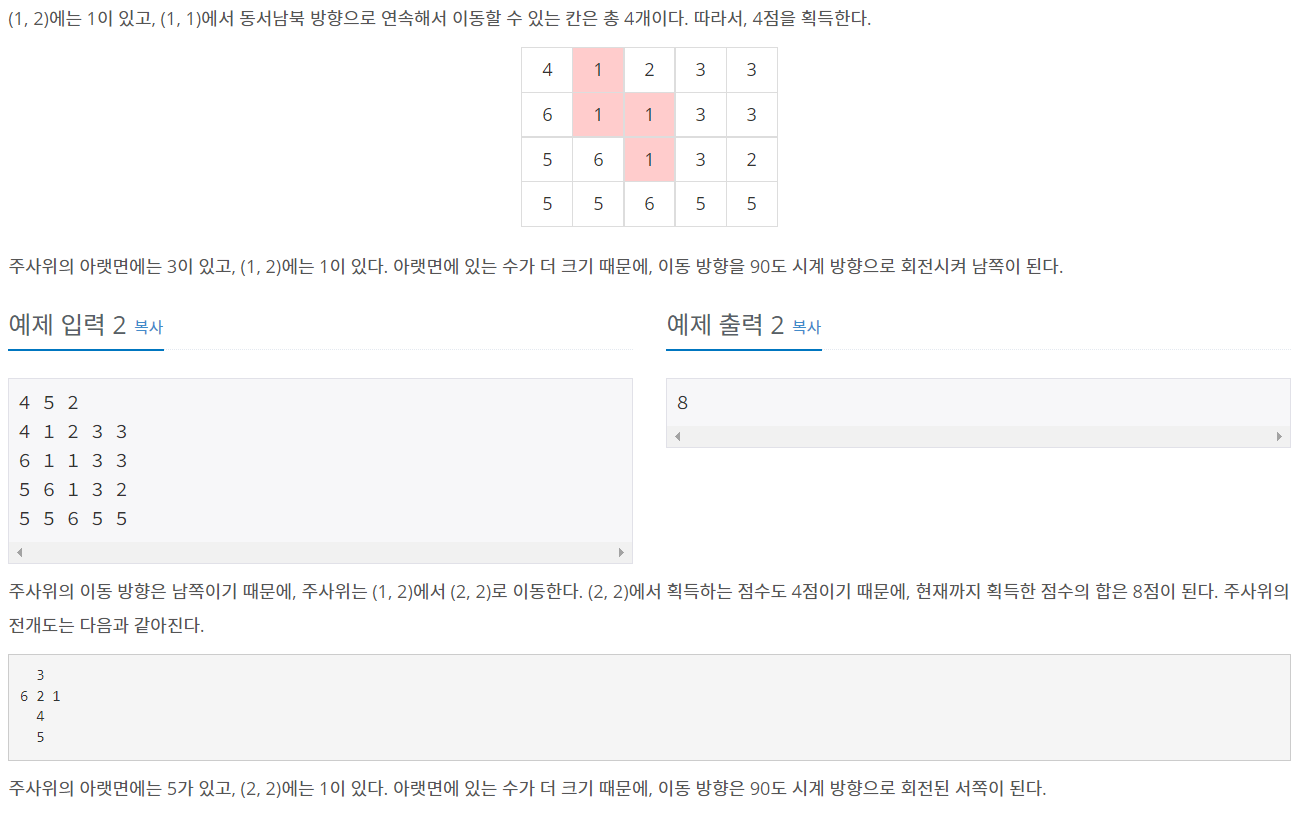
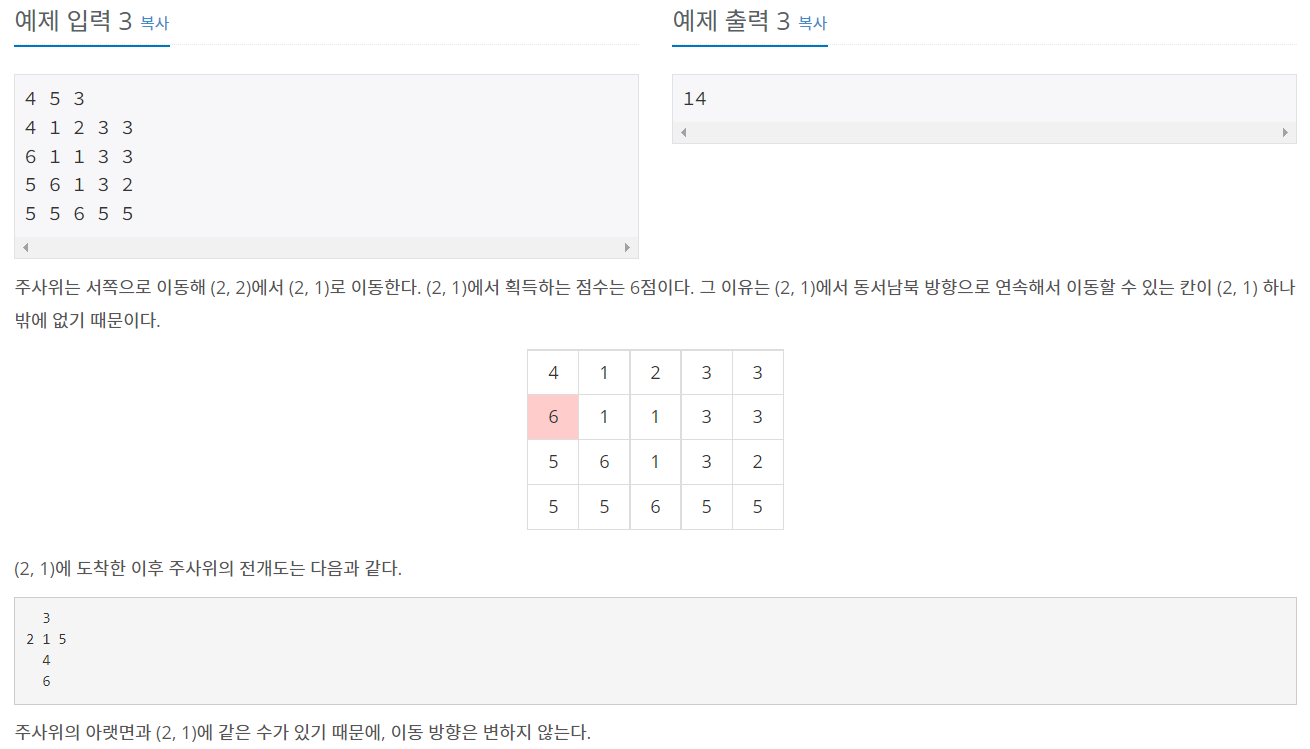
크기가 N×M인 지도가 존재한다. 지도의 오른쪽은 동쪽, 위쪽은 북쪽이다. 지도의 좌표는 (r, c)로 나타내며, r는 북쪽으로부터 떨어진 칸의 개수, c는 서쪽으로부터 떨어진 칸의 개수이다. 가장 왼
www.acmicpc.net
[ 시뮬레이션 + BFS ]
이번 문제 또한 아주 친절하게 문제가 설명하는대로만 짜면 되는 문제이다..
그런데 주사위 방향을 어떻게 매번 돌릴지...? 를 너무 오랫동안 고민했다 🤣
int dice[7] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 };
int d1 = dice[1];
int d2 = dice[2];
int d3 = dice[3];
int d4 = dice[4];
int d5 = dice[5];
int d6 = dice[6];
if (d == 0)
{
dice[1] = d4;
dice[2] = d2;
dice[3] = d1;
dice[4] = d6;
dice[5] = d5;
dice[6] = d3;
}
else if (d == 1)
{
dice[1] = d3;
dice[2] = d2;
dice[3] = d6;
dice[4] = d1;
dice[5] = d5;
dice[6] = d4;
}
else if (d == 2)
{
dice[1] = d2;
dice[2] = d6;
dice[3] = d3;
dice[4] = d4;
dice[5] = d1;
dice[6] = d5;
}
else
{
dice[1] = d5;
dice[2] = d1;
dice[3] = d3;
dice[4] = d4;
dice[5] = d6;
dice[6] = d2;
}그래서 위에처럼 각각 index
1 : 윗면
2 : 뒷면
3 : 오른쪽면
4 : 왼쪽면
5 : 앞면
6 : 아랫면
으로 배열을 만들어서 저장했고, 방향이 바뀔때마다 위에처럼 if문을 써서 각각 인덱스를 바꿔줬다.
이 부분 말고는 크게 어려운 부분은 없는듯 하다.
점수획득 부분도 다른 문제 유형과 같이 BFS로 인접한 칸을 찾아주면 된다 :)
*memset 쓸 때 꼭 memory.h include 해주기.. 안하면 백준에선 컴파일에러남.......🤣
(실제로 삼성 코테에서도 에러 나는지 궁금...)
<전체코드>
#include <iostream>
#include <queue>
#include <memory.h>
using namespace std;
int N, M, K;
const int MAX = 21;
int map[MAX][MAX];
bool visit[MAX][MAX];
int dice[7] = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6 };
//이동 방향 : 동 서 남 북
int dy[4] = { 0,0,1,-1 };
int dx[4] = { 1,-1,0,0 };
int y = 1;
int x = 1;
//주사위 방향
int d = 0;
int score = 0;
int iter;
void roll_dice()
{
//주사위가 이동 방향으로 한 칸 굴러간다. 만약, 이동 방향에 칸이 없다면, 이동 방향을 반대로 한 다음 한 칸 굴러간다.
int ny = y + dy[d];
int nx = x + dx[d];
if (ny < 1 || nx < 1 || ny > N || nx > M)
{
if (d == 0)
d = 1;
else if (d == 1)
d = 0;
else if (d == 2)
d = 3;
else
d = 2;
ny = y + dy[d];
nx = x + dx[d];
}
y = ny;
x = nx;
}
void get_score(int y, int x)
{
//주사위가 도착한 칸 (x, y)에 대한 점수를 획득한다.
//칸 (x, y)에 대한 점수는 다음과 같이 구할 수 있다. (x, y)에 있는 정수를 B라고 했을때, (x, y)에서 동서남북 방향으로 연속해서 이동할 수 있는 칸의 수 C를 모두 구한다.
//이때 이동할 수 있는 칸에는 모두 정수 B가 있어야 한다. 여기서 점수는 B와 C를 곱한 값이다.
int cnt = 1;
int s = map[y][x];
//bool visit[MAX][MAX] = { false, };
memset(visit, false, sizeof(visit));
queue<pair<int, int>> q;
q.push(make_pair(y, x));
visit[y][x] = true;
while (!q.empty())
{
y = q.front().first;
x = q.front().second;
q.pop();
for (int dir = 0; dir < 4; dir++)
{
int ny = y + dy[dir];
int nx = x + dx[dir];
if (ny < 1 || nx < 1 || ny > N || nx > M) continue;
if (s == map[ny][nx] && !visit[ny][nx])
{
cnt++;
q.push(make_pair(ny, nx));
visit[ny][nx] = true;
}
}
}
score += (s * cnt);
}
void decision_direction(int d)
{
int d1 = dice[1];
int d2 = dice[2];
int d3 = dice[3];
int d4 = dice[4];
int d5 = dice[5];
int d6 = dice[6];
if (d == 0)
{
dice[1] = d4;
dice[2] = d2;
dice[3] = d1;
dice[4] = d6;
dice[5] = d5;
dice[6] = d3;
}
else if (d == 1)
{
dice[1] = d3;
dice[2] = d2;
dice[3] = d6;
dice[4] = d1;
dice[5] = d5;
dice[6] = d4;
}
else if (d == 2)
{
dice[1] = d2;
dice[2] = d6;
dice[3] = d3;
dice[4] = d4;
dice[5] = d1;
dice[6] = d5;
}
else
{
dice[1] = d5;
dice[2] = d1;
dice[3] = d3;
dice[4] = d4;
dice[5] = d6;
dice[6] = d2;
}
}
void change_direction()
{
//주사위의 아랫면에 있는 정수 A와 주사위가 있는 칸 (x, y)에 있는 정수 B를 비교해 이동 방향을 결정한다
//A > B인 경우 이동 방향을 90도 시계 방향으로 회전시킨다.
//A < B인 경우 이동 방향을 90도 반시계 방향으로 회전시킨다.
//A = B인 경우 이동 방향에 변화는 없다.
if (dice[6] > map[y][x])
{
if (d == 0)
d = 2;
else if (d == 1)
d = 3;
else if (d == 2)
d = 1;
else
d = 0;
}
else if (dice[6] < map[y][x])
{
if (d == 0)
d = 3;
else if (d == 1)
d = 2;
else if (d == 2)
d = 0;
else
d = 1;
}
}
int main()
{
ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(NULL);
cout.tie(NULL);
cin >> N >> M >> K;
for (int y = 1; y <= N; y++)
{
for (int x = 1; x <= M; x++)
{
cin >> map[y][x];
}
}
for (iter = 0; iter < K; iter++)
{
roll_dice();
decision_direction(d);
change_direction();
get_score(y, x);
}
cout << score << "\n";
return 0;
}'알고리즘 > 삼성 기출' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준/C++] 21610번 마법사 상어와 비바라기 - 삼성SW기출 (0) | 2022.04.04 |
|---|---|
| [백준/C++] 23289번 온풍기 안녕! -삼성SW기출 (0) | 2022.04.04 |
| [백준/C++] 23290번 마법사 상어와 복제 - 삼성SW기출 (0) | 2022.03.30 |
| [백준/C++] 14502번 연구소 - 삼성 SW 기출 (0) | 2022.02.28 |
| [백준/C++] 13460번 구슬 탈출2 - 삼성SW기출 (0) | 2022.02.03 |